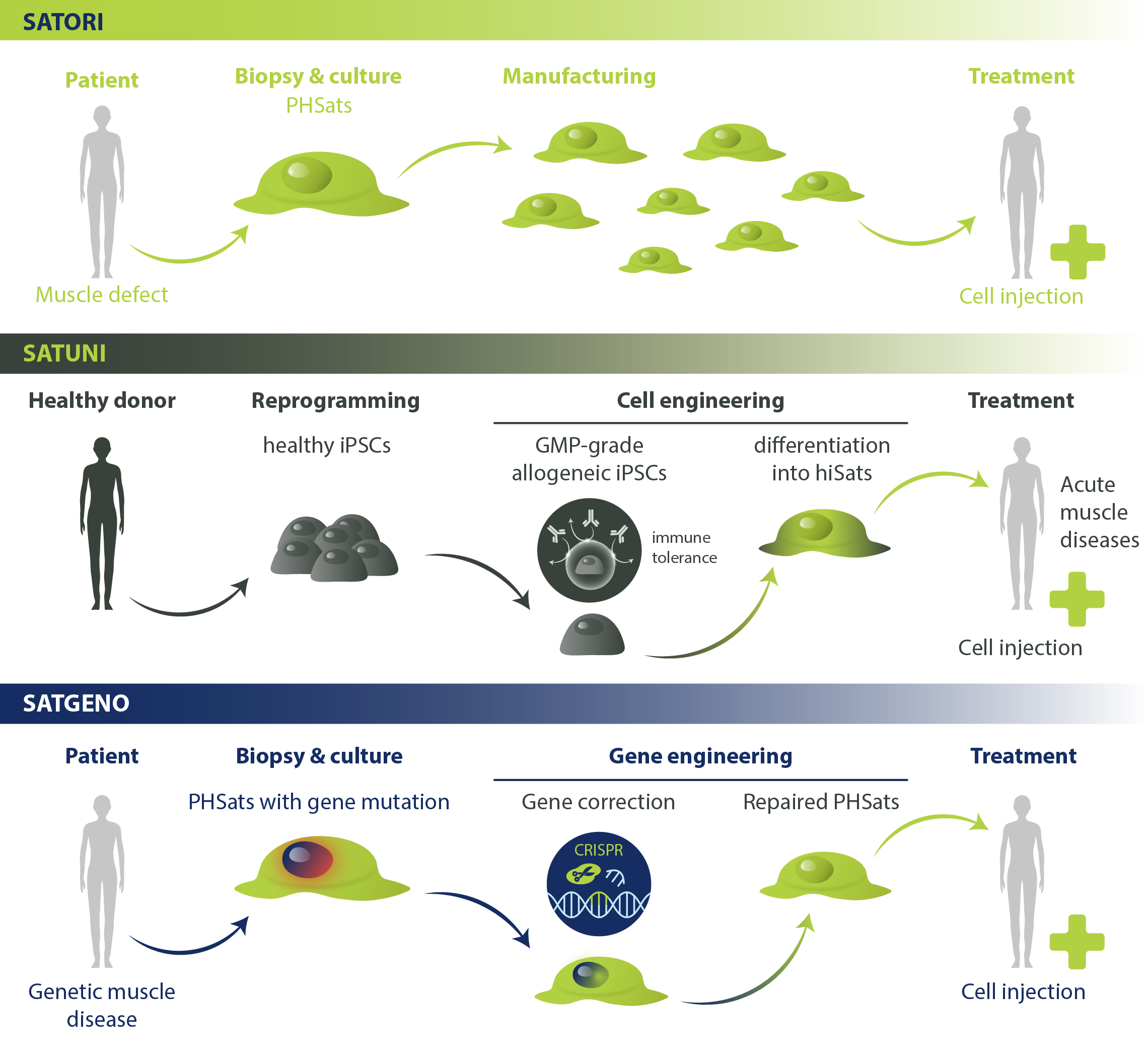
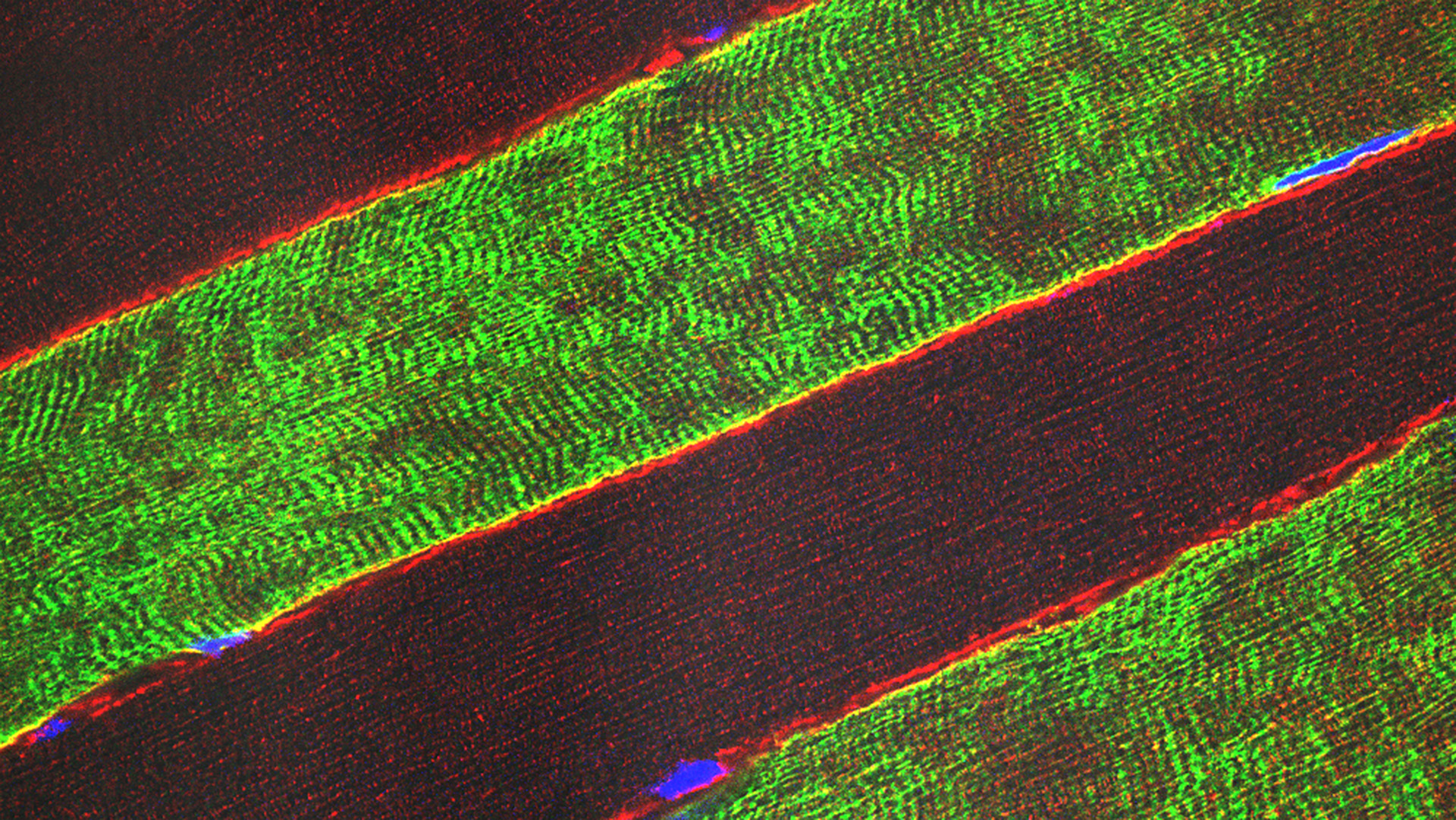
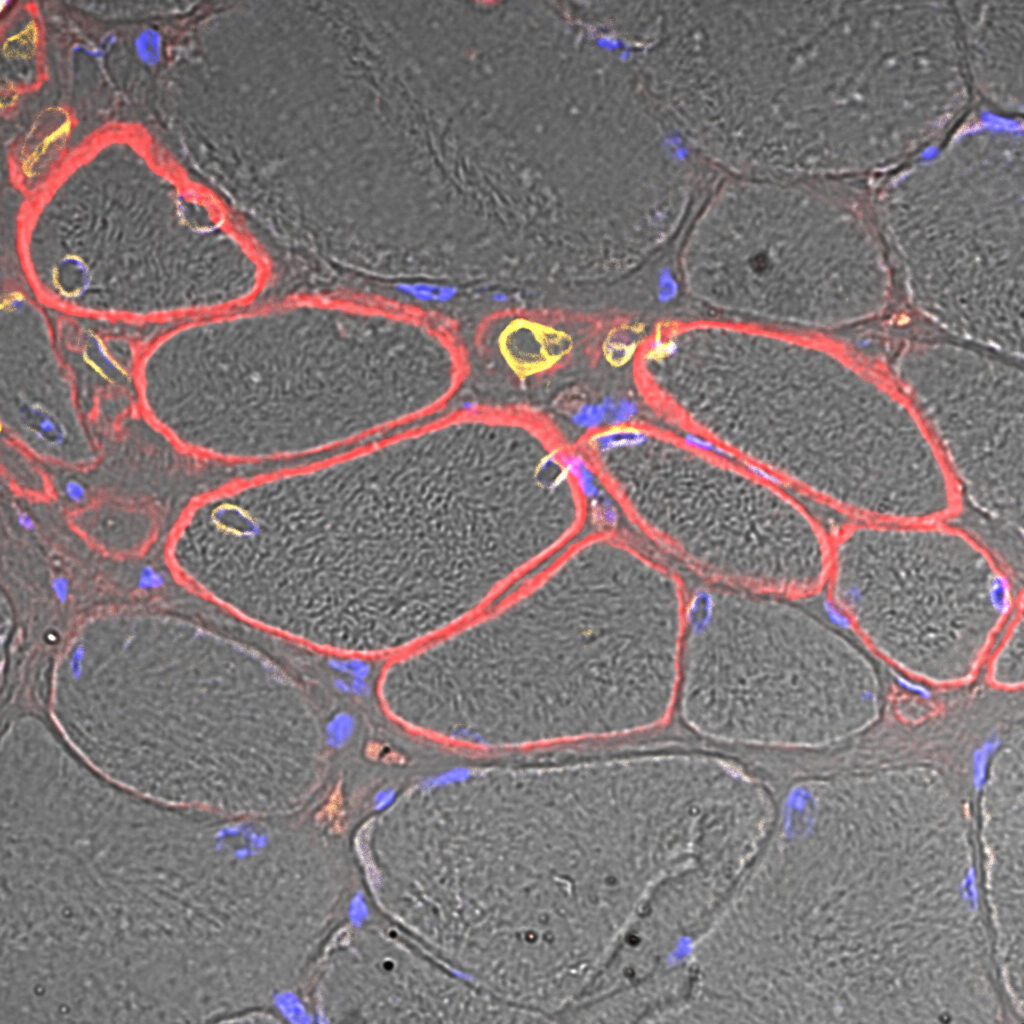
Satori: Autologous PHSats therapy to treat local muscle defects. From a small muscle specimen, the patient’s own muscle stem cells are isolated and expanded using our innovative PHSats technology. The Satori product is delivered to the hospital in a ready-to-use formulation.
Satuni: Allogeneic therapy with engineered PHSats to treat acute muscle wasting. Human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) are engineered so that they are not targeted by the recipient’s immune system. From these, we induce the PHSats phenotype. Satuni products are manufactured in large non-patient-specific batches.
Satgeno: Autologous therapy with genetically corrected PHSats to treat muscular dystrophies. The disease-causing mutation in the isolated cell population is repaired with specific gene editing tools. The repaired population is expanded with our PHSats technology and injected into selected affected muscles to build healthy muscle tissue.